Search Engine Optimization (SEO)

Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is a crucial process aimed at enhancing a website’s visibility in organic search results, thereby increasing traffic. The goal is to improve a website’s position in search engine results pages, ensuring that more people see it. Key activities in effective SEO include identifying relevant keywords with high search traffic, creating high-quality and user-friendly content optimized for search engines, incorporating relevant links from reputable sites, and measuring the results. In today’s digital landscape, SEO is widely recognized as an essential marketing activity for online success.
Paid and organic search similarities:
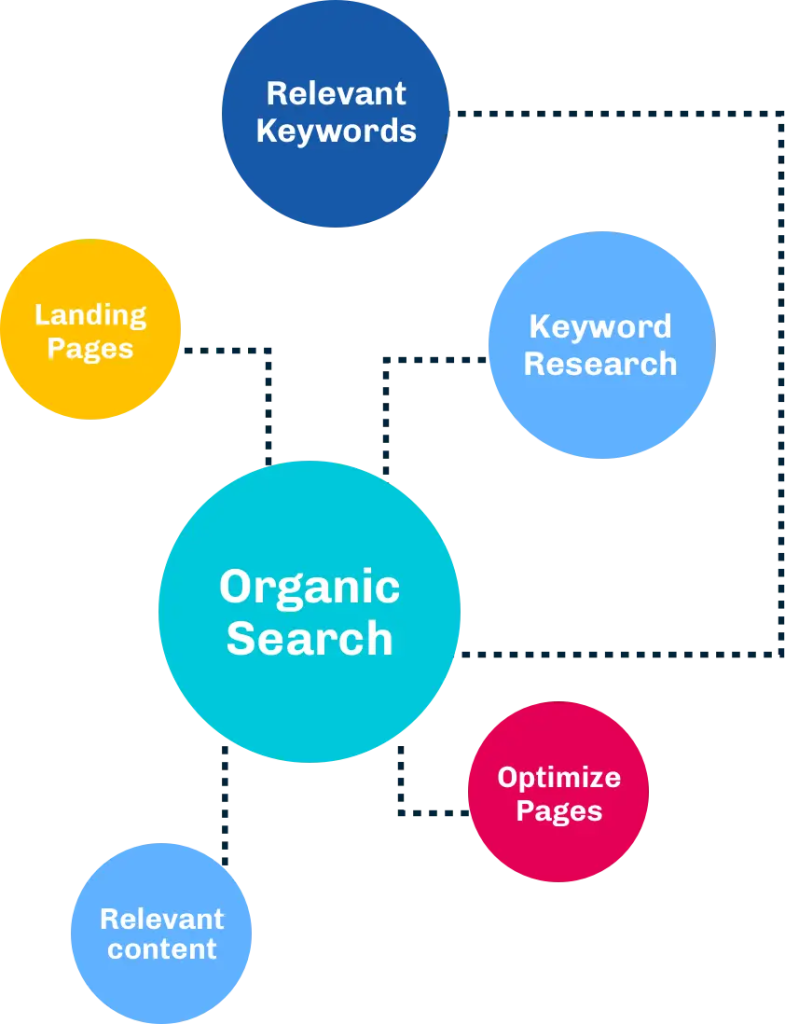
Keyword Research: Both paid and organic search involve users entering keywords into search engines. Keyword research is essential for optimizing content and ads to align with user search queries in both paid and organic search strategies.
Landing Pages: Both types of search require the creation of landing pages. In SEO, the landing page is connected to the website, while in paid search, it can be the same as the organic landing page or a separate stand-alone page.
Traffic: Generating traffic is a primary objective in both paid and organic search. Both types of search traffic involve users actively seeking information or answers, demonstrating user intent. This active mindset increases the likelihood of user engagement and action.
The distinctions between paid and organic search are significant:
- Position: Paid search results appear at the top of search engine results pages, while organic results are positioned below them.
- Time: Paid search yields nearly instant results, often within minutes, whereas organic search takes longer, ranging from weeks to months or even years.
- Payment: Paid search involves paying for traffic through a pay-per-click (PPC) model, where a fee is incurred for each user click. Organic search traffic is free but demands an investment of time and resources.
- ROI: Measuring return on investment is more straightforward in paid search due to accessible keyword data. However, paid search ROI can plateau or decline over time. Organic search ROI is harder to measure but often improves in the long term, providing a solid return.
- Share of Traffic: Approximately 20-30% of searchers click on paid results, while 70-80% prefer organic results. The majority of clicks go to organic search results.

The three pillars of SEO are crucial for digital marketers to understand and consistently implement:-

(i)Technical Optimization: Technical Optimization involves activities on a website aimed at improving SEO but is not directly related to content. These optimizations often occur behind the scenes. Addressing technical aspects ensures that search engines can effectively crawl, index, and understand the content of a website.
(ii)On-Page Optimization: On-Page Optimization focuses on ensuring that the content on a website is relevant and provides an excellent user experience. This includes incorporating the right keywords within the content. On-Page Optimization can be executed through content management systems like WordPress, Wix, Drupal, Joomla, Magento, Shopify, and Expression Engine.
(iii)Off-Page Optimization: Off-Page Optimization involves activities outside the website that aim to enhance its search engine rankings. The primary driver is building a strong backlink profile, contributing to the site’s reputation. Off-Page Optimization is crucial for demonstrating the website’s authority and credibility to search engines.
Search engines operate through a three-step process: crawling, indexing, and ranking.
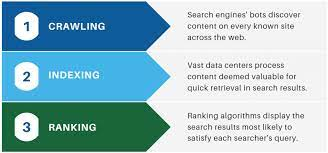
(i)Crawling: Search engines deploy web crawlers, often called spiders or robots, to discover new web pages and update information on existing ones. Crawlers follow links on web pages to find new content. For example, if a blog post is linked from a homepage, the crawler will navigate to the blog post during its crawl.
(ii)Indexing: Indexing involves the search engine deciding whether to use the crawled content. If deemed valuable, the page is added to the search engine’s index, a database used in the ranking process.Pages are typically included in the index if they offer unique and valuable content. Exclusions may occur for duplicate, low-value, or spammy content, as well as pages with crawling issues or lacking inbound links.
(iii)Ranking: Ranking is the crucial step that occurs after crawling and indexing. Search engines use over 200 ranking signals categorized under the three pillars of SEO (technical optimization, on-page optimization, and off-page optimization) to determine the order of search results.
Examples of Ranking Signals:
- Keyword presence in the title tag.
- Loading speed and mobile-friendliness of the web page.
- Website reputation and credibility on the searched topic.
How does SEO work?
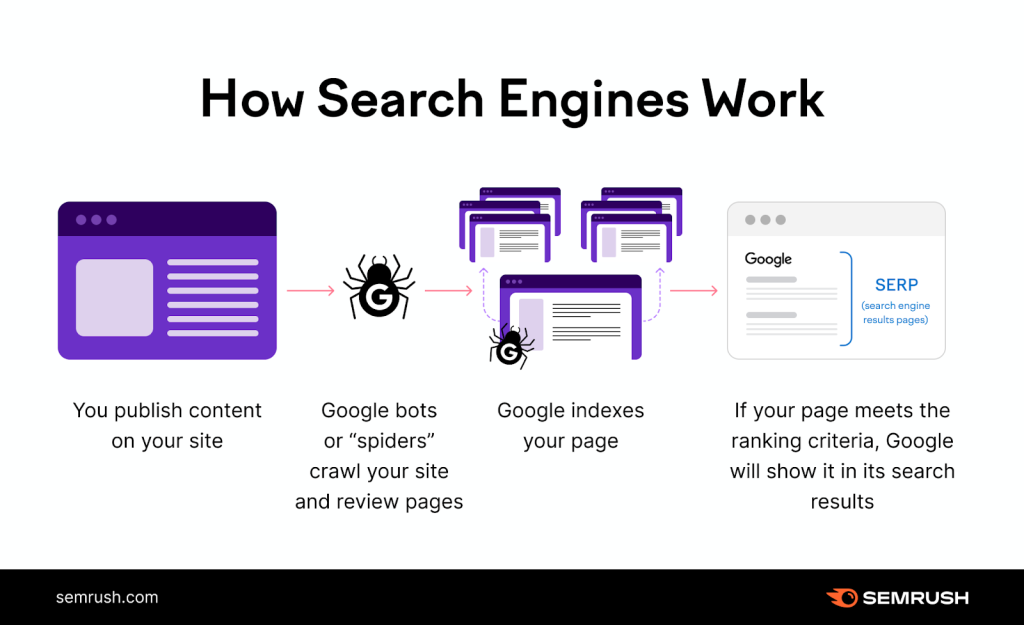
1. Keyword Research: Keyword research is a fundamental aspect of SEO (Search Engine Optimization) that involves identifying and analyzing the words and phrases users type into search engines. The goal is to understand user intent and optimize content to rank higher in search engine results for those specific queries. Keywords, also known as SEO keywords, play a crucial role in establishing and optimizing online content. From the perspective of potential customers, keywords are the words and phrases they enter into search bars to find products, services, or answers to their queries. For marketers, the careful selection and inclusion of keywords in content serve to inform search engines about the content of webpages, influencing rankings and visibility.
(i)Understand Your Business and Audience(ii)Brainstorm Seed Keywords(iii)Use Keyword Research Tools(iv)Long-Tail Keywords(v)Competitor Analysis(vi)User Intent(vii)Group Keywords(viii)Prioritize Keywords(ix)Check SERP Features(x)Regularly Review and Update.
2. On-Page SEO: On-page SEO, or on-site SEO, involves optimizing the content of a webpage to improve its visibility and relevance to both users and search engines. Key tasks in on-page SEO include aligning content with search intent, optimizing title tags, managing internal links, and refining URLs. The goal is to present content that matches user queries and, when deemed useful, ranks higher in search engine results.
3. Quality Content: Create high-quality, valuable, and relevant content that satisfies the user’s intent. Search engines aim to deliver the best possible results to their users, so high-quality content is crucial for good SEO. The subjectivity of quality is inherent in the diverse preferences and needs of the audience. (i)Subjectivity of Quality(ii)Better Than Existing Content(iii)User-Centric Approach(iv)Usability and Memorability(v)Likelihood of Sharing.
4. Link Building: Link building is a strategic practice in SEO involving the acquisition of one-way hyperlinks (backlinks) to a website, with the primary objective of enhancing search engine visibility. Various link-building strategies are employed, including content marketing, the creation of useful tools, email outreach, broken link-building, and public relations. The historical context of link building dates back to the pre-Google era when search engines like Yahoo! and Alta Vista dominated the landscape. During this time, search results were primarily ranked based on the content of web pages. However, Google’s introduction of the PageRank Algorithm revolutionized the approach. Instead of solely analyzing content, Google considered the number of links pointing to a page as a crucial factor. Over the years, links have remained a fundamental ranking signal, contributing significantly to Google’s assessment of a webpage’s quality. (i)Evolution of Search Engines(ii)Persistence of Links as a Ranking Signal(iii)Shift to Link Quality(iv)Upcoming Focus on High-Quality Links.
5. Technical SEO: Technical SEO is a critical aspect of website optimization that focuses on enhancing a site’s performance for search engines, with additional consideration for improving user experience. Key tasks associated with technical SEO include submitting sitemaps to Google, creating an SEO-friendly site structure, improving website speed, ensuring mobile-friendliness, and addressing issues such as duplicate content. (i)Objectives of Technical SEO(ii)Common Technical SEO Tasks(iii)Impact on Search Engine Rankings(iv)Importance of Page Speed and Mobile-Friendliness(v)User Experience Signals(vi)Business Impact.
6. User Experience: User Experience, commonly abbreviated as UX, refers to how a user interacts with a product or system. It is a fundamental aspect of good website design, encompassing the overall experience and satisfaction users derive from their interaction with a website or any other digital product. Effective UX design aims to create positive, intuitive, and enjoyable experiences for users, considering aspects such as usability, accessibility, and the emotional response of users during their interaction with the product or system. (i)Usability Experience(ii)Accessibility Experience(iii)Desirability Experience(iv)Credibility Experience(v)Findability Experience(vi)Learnability Experience(vii)Satisfaction Experience(viii)Accessibility Experience(ix)Efficiency Experience(x)Engagement Experience.
7. Social Signals: Social signals refer to metrics such as shares, likes, votes, and retweets on social media platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter. These metrics reflect human interactions with content on social media and have been a topic of discussion in the SEO community regarding their impact on search engine rankings. (i)Lack of Official Confirmation(ii)Potential Indirect Influence(iii)Brand Visibility and Authority(iv)Social Content Indexing(v)Social Profiles in Search Results(vi)User Engagement and Click-Through Rates(vii)Content Amplification(viii)Google+ Shutdown.
8. Monitoring and Adjusting: Monitoring and adjusting are crucial aspects of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) to ensure that your website continues to perform well in search engine results. Regularly monitor your website’s performance using analytics tools. Track keyword rankings, organic traffic, and user engagement. Use this data to identify areas for improvement and adjust your SEO strategy accordingly. (i)Monitoring Performance Metrics(ii)Keyword Performance(iii)Content Performance(iv)Backlink Analysis(v)Technical SEO Audits(vi)User Experience (UX) Evaluation(vii)Competitor Analysis(viii)Algorithm Updates(ix)Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO)(x)Local SEO Monitoring(xi)Adjusting Strategies(xii)Regular Reporting.