Healthcare has entered a new era where digital advancements are reshaping how medical services are delivered. Among these innovations, Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands out as a transformative force, driving groundbreaking improvements in patient care, diagnosis, treatment, and operational efficiency. AI’s potential in healthcare goes far beyond automation; it leverages complex algorithms, machine learning, and data analytics to enable healthcare providers to make more accurate, timely, and data-driven decisions, resulting in better patient outcomes and reduced costs.
In recent years, the explosion of healthcare data—ranging from electronic health records and medical imaging to genetic information and real-time patient data from wearable devices—has presented new opportunities and challenges. AI tools have proven essential in managing and interpreting this wealth of information, using predictive analytics, natural language processing, and image recognition to detect patterns and provide insights that were previously unimaginable. AI can identify early warning signs of diseases, customize patient treatment plans, and assist in the development of new drugs, all of which are reshaping the healthcare landscape.
For healthcare providers, AI not only supports clinical decisions but also streamlines administrative processes, reducing the burden of paperwork and routine tasks, which in turn allows them to spend more time focusing on patient care. From triaging emergency cases to automating insurance claims processing, AI-powered tools have shown significant promise in transforming healthcare operations. Patients, too, benefit from AI through applications like chatbots for symptom checking, virtual health assistants, and personalized health recommendations, creating a more engaging and responsive healthcare experience.
With the immense promise AI holds, healthcare systems worldwide are investing heavily in AI-powered solutions to make healthcare more accessible, efficient, and inclusive. This article dives into the critical areas where AI tools are having the most impact, discussing their applications in diagnostics, predictive analytics, patient engagement, drug discovery, surgical assistance, and more. We will also explore the advantages these tools bring to healthcare, the challenges and ethical considerations in deploying them, and the promising future they herald for patient care and public health on a global scale.
Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Patient Care, Diagnosis, and Beyond
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a pivotal force in reshaping healthcare, offering solutions that improve patient outcomes, streamline administrative tasks, and assist healthcare providers in making precise and timely decisions. From predictive analytics to patient engagement, AI is enhancing every aspect of healthcare. This article explores the key areas where AI tools are most impactful in healthcare, highlighting their applications, advantages, and the future they promise.
1. AI-Driven Diagnostics: Accurate and Swift Diagnosis
Applications: AI models, particularly those based on deep learning, have significantly improved diagnostic accuracy. They analyze complex medical data like MRI, CT scans, and X-rays, identifying patterns and anomalies faster than human interpretation alone.
Notable AI Tools:
- PathAI: PathAI’s algorithms help pathologists improve diagnostic accuracy for diseases like cancer by analyzing pathology images.
- Aidoc: Aidoc provides real-time support for radiologists by flagging critical cases, such as strokes or brain hemorrhages, for faster intervention.
Impact: AI diagnostic tools decrease the risk of misdiagnosis, which can lead to severe consequences. By aiding specialists, these tools also reduce burnout, allowing more focus on complex cases.
2. Predictive Analytics for Preventative Care
Applications: Predictive analytics tools analyze historical and real-time patient data to identify individuals at high risk for conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. By doing so, healthcare providers can initiate preventive measures before issues become critical.
Notable AI Tools:
- IBM Watson Health: By harnessing the power of IBM’s Watson, healthcare professionals gain insights into patient data, predicting disease risks.
- Google DeepMind: This AI tool has shown impressive results in predicting acute kidney injury up to 48 hours before it happens.
Impact: Predictive analytics in healthcare enables early intervention, which improves patient outcomes and reduces costs by avoiding emergency treatment.
3. Enhanced Patient Engagement and Care through AI Chatbots
Applications: AI-powered chatbots provide round-the-clock support, answering questions, scheduling appointments, and even reminding patients about medication. These virtual assistants improve patient satisfaction and reduce hospital readmission rates.
Notable AI Tools:
- Buoy Health: A chatbot-driven tool that guides users through symptoms, suggesting possible diagnoses and next steps.
- Babylon Health: Babylon offers AI-driven consultations that assess symptoms and provide information to patients about potential treatment options.
Impact: Chatbots allow healthcare providers to handle patient inquiries efficiently, reserving resources for complex cases while ensuring patients receive the information and support they need.
4. Drug Discovery and Development: Faster and More Accurate
Applications: AI accelerates the drug discovery process by analyzing biological data, modeling molecular structures, and predicting how drugs interact with the body. Machine learning models identify viable drug candidates quickly, potentially reducing development costs and timelines.
Notable AI Tools:
- BenevolentAI: By integrating biomedical knowledge, BenevolentAI assists researchers in identifying new drug compounds.
- Atomwise: Atomwise uses deep learning to predict drug efficacy, targeting diseases from Ebola to COVID-19.
Impact: AI-driven drug discovery opens pathways to more effective treatments and cures for previously untreatable diseases. It enables pharmaceutical companies to bring life-saving drugs to market faster, improving public health outcomes globally.
5. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) for Administrative Efficiency
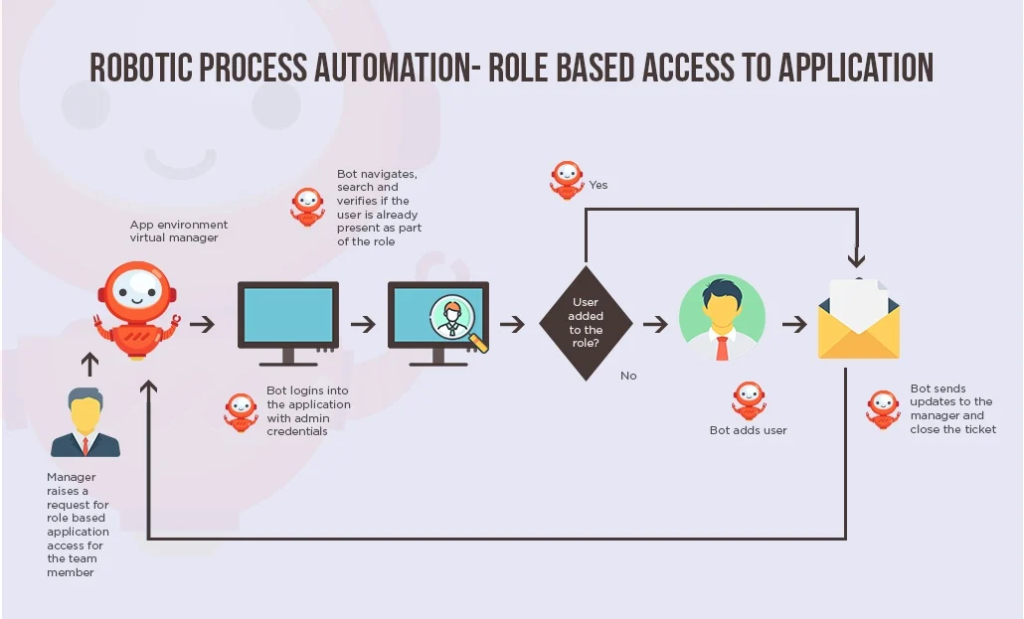
Applications: Robotic Process Automation (RPA) manages repetitive tasks such as data entry, billing, and scheduling. By automating these tasks, healthcare facilities reduce human error and enhance productivity, allowing healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
Notable AI Tools:
- UiPath: UiPath’s RPA solutions streamline administrative workflows, from billing to scheduling, enhancing operational efficiency.
- Automation Anywhere: This tool provides bots that handle repetitive tasks, including patient registration and insurance verification.
Impact: RPA in healthcare minimizes clerical errors, enhances data accuracy, and saves valuable time for healthcare providers, enabling more resources for patient-facing services.
6. Personalized Treatment Plans with AI-Based Precision Medicine
Applications: Precision medicine uses AI to analyze genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors unique to each patient, crafting tailored treatment plans. This individualized approach is particularly effective for treating complex diseases, such as cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Notable AI Tools:
- Tempus: A precision medicine company that uses AI to analyze patient data and develop personalized treatment options.
- Oncora Medical: Specializing in oncology, Oncora Medical leverages machine learning to tailor treatment plans for cancer patients.
Impact: AI-based precision medicine enhances treatment efficacy by ensuring that patients receive therapies tailored to their specific conditions, genetics, and lifestyles, reducing adverse effects and improving recovery rates.
7. AI in Surgery: Enhancing Accuracy and Outcomes
Applications: Robotic surgery assisted by AI tools improves precision, particularly for minimally invasive surgeries. AI monitors a surgeon’s hand movements and provides real-time feedback to enhance accuracy during procedures.
Notable AI Tools:
- Da Vinci Surgical System: This AI-assisted robotic system helps surgeons perform complex procedures with greater precision.
- Mazor Robotics: Focused on spinal surgery, Mazor’s AI-powered robotics provide guidance during complex operations.
Impact: AI-guided surgeries reduce recovery times and minimize post-surgical complications, leading to faster patient discharge and reduced hospital costs.
8. Disease Surveillance and Public Health Management
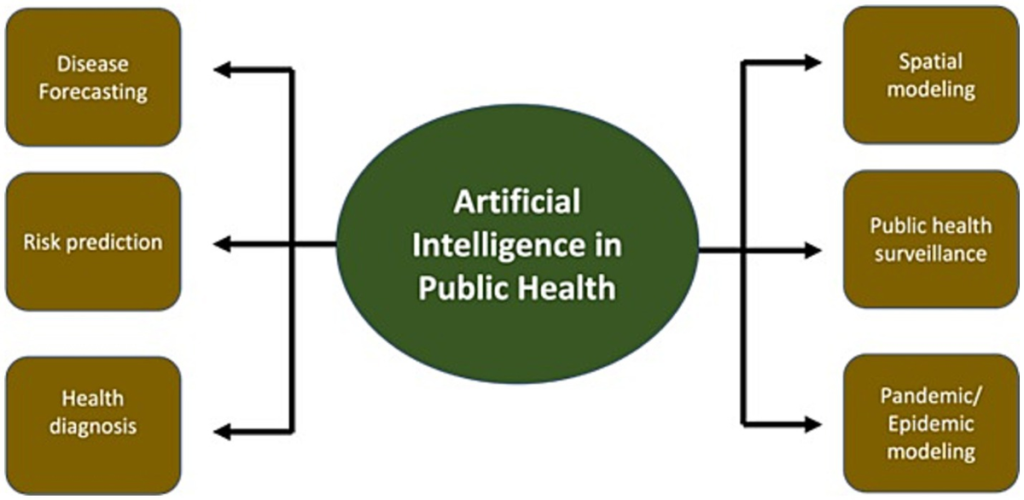
Applications: AI helps in monitoring and predicting outbreaks by analyzing data from various sources, such as social media, healthcare records, and environmental data, allowing public health officials to prepare for potential epidemics.
Notable AI Tools:
- BlueDot: BlueDot’s AI was one of the first to alert authorities about the COVID-19 outbreak, showcasing the potential for early warning systems in disease surveillance.
- HealthMap: Developed by Boston Children’s Hospital, HealthMap collects data from social media and news reports to track disease outbreaks globally.
Impact: AI-based disease surveillance tools help prevent the spread of infectious diseases, improving response times and allowing for proactive public health measures.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI Healthcare
While the benefits of AI in healthcare are transformative, they also bring complex challenges and ethical questions that require careful consideration and management. As AI increasingly integrates into healthcare, providers, regulators, and technologists must address these critical concerns to ensure that AI usage remains transparent, fair, and safe for all patients. Below are some key challenges:
- Data Privacy and Security
AI applications in healthcare rely on large datasets, often containing highly sensitive patient information. Protecting this data is essential, as breaches can lead to severe consequences, from identity theft to misuse of medical information. Ensuring data privacy goes beyond encryption and involves stringent policies that dictate how data can be accessed, stored, and shared across AI systems. Compliance with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States adds another layer of complexity, as healthcare providers must navigate these laws while implementing AI solutions. - Bias and Fairness
AI algorithms are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. If AI models are built using data that reflects historical biases, these biases may be perpetuated or even amplified, resulting in unfair treatment recommendations for certain groups. For example, studies have shown that certain AI tools may perform differently across racial or gender lines, leading to unequal care. Ensuring fairness requires diverse, representative datasets and a thorough examination of AI outputs to prevent discriminatory patterns. Researchers and developers must collaborate to create frameworks and standards to regularly audit AI tools for potential biases. - Transparency and Explainability
Many AI algorithms, especially those based on deep learning, operate as “black boxes,” meaning their decision-making processes can be difficult to interpret. In healthcare, understanding why an AI tool makes a specific recommendation is critical to gaining trust from healthcare providers and patients. Without this transparency, healthcare professionals may be hesitant to rely on AI for critical decisions. Developing explainable AI models that allow clinicians to understand and validate AI-driven insights is a significant focus area to build trust and ensure effective clinical integration. - Accountability and Liability
When an AI system is involved in patient care, determining accountability becomes challenging, especially if errors or adverse outcomes arise. Questions around liability—whether it falls on the AI developers, the healthcare institution, or the medical professional using the AI tool—are still being debated. Establishing clear guidelines on accountability is crucial to protect both patients and healthcare providers. - Integration with Existing Systems
Healthcare providers face difficulties in integrating new AI tools with legacy systems and electronic health record (EHR) platforms. Seamless integration is vital for AI to deliver meaningful insights without disrupting workflows. As AI tools evolve, interoperability standards will be essential to enable smooth communication between new and existing healthcare technologies, reducing friction in adoption and maximizing AI’s potential benefits.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
As AI continues to mature, its impact on healthcare is expected to deepen, making healthcare more personalized, efficient, and inclusive. Here’s a look at some of the exciting advancements on the horizon:
- Personalized Medicine through Genomics and Precision Medicine
AI is transforming genomics and precision medicine by allowing for in-depth analysis of a patient’s genetic makeup to identify individualized treatments. For instance, AI can help pinpoint specific gene mutations linked to diseases like cancer, enabling tailored therapies that improve treatment efficacy and minimize side effects. The future of healthcare lies in precision medicine, where AI assists in creating highly personalized treatments that cater to the unique genetic profile of each patient. - Early Diagnosis and Predictive Healthcare
AI’s ability to analyze large datasets in real-time is paving the way for early diagnosis and preventive care. AI models are increasingly used to predict disease onset by analyzing patterns in medical histories and lifestyle factors. For example, predictive algorithms could identify high-risk patients for conditions like heart disease or diabetes years before symptoms arise. With this early insight, healthcare providers can implement preventive measures, potentially reducing the incidence of severe health complications and enhancing patient outcomes. - Mental Health Support and Monitoring
The field of mental health is ripe for AI-driven innovations. AI-powered tools are being developed to monitor behavioral changes, assess mental health conditions, and provide support through virtual counseling. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze speech patterns or social media activity to detect signs of depression or anxiety, enabling timely interventions. Virtual mental health assistants and chatbots can provide round-the-clock support, ensuring patients have access to resources and help, even outside traditional healthcare settings. - Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
Telemedicine and AI-driven remote monitoring tools are likely to become staples of future healthcare, especially in rural or underserved areas where access to medical care is limited. AI can monitor vital signs and health data from wearable devices, providing continuous assessments of a patient’s health status and alerting healthcare providers if any issues arise. This level of monitoring will improve patient engagement, enable early detection of health risks, and reduce hospital visits by allowing patients to manage their health from home. - AI-Assisted Robotics in Surgery
Robotic surgery, augmented by AI, will continue to gain popularity, enabling precise, minimally invasive procedures that reduce recovery times. AI-assisted robotic systems analyze vast datasets from previous surgeries, giving surgeons guidance and enhancing accuracy during procedures. This innovation not only improves patient outcomes but also opens possibilities for remote surgeries, where top surgeons can operate on patients in distant locations. - AI in Public Health and Epidemic Management
AI tools are already proving essential in tracking and predicting disease outbreaks, as seen with COVID-19. In the future, AI’s role in public health will expand, helping authorities monitor and predict epidemic patterns, allocate resources effectively, and prevent widespread transmission. AI-powered platforms can analyze data from various sources—social media, news, health reports—to provide early warnings and enable rapid response, minimizing the impact of future pandemics.